If you don’t have high blood pressure by age 55, your chance of developing it at some point in your life is a 90 percent, according to the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute.
The most common side effects with ARBs are cough, elevated potassium levels, low blood pressure, dizziness, headache, drowsiness, diarrhea, abnormal taste sensation (salty or metallic taste), and rash. The most serious, but rare side effects are kidney failure, liver failure, allergic reactions, a decrease in white blood cells, and swelling of tissues (angioedema).
In a 90-95 percent of cases, research scientists don’t know what causes high blood pressure, but fortunately they know enough to have developed both drug and non-drug products to treat it effectively.
While most people can tolerate ACE Inhibitors, some may experience side effects such as cough, elevated blood potassium levels, low blood pressure, dizziness, headache, drowsiness, weakness, abnormal taste (salty or metallic taste), and rash. Rare, but more serious side effects include kidney failure, allergic reactions, a decrease in white blood cells, and swelling of tissues (angioedema).
In Part 2 of our Blood Pressure Research Report we will discuss the ACE Inhibitors and Angiotension Receptor Blockers, Natural Therapy for Maintaining Healthy Blood Pressure and benefits of Bioactive Casein Hydrolysate Tripeptides VPP and IPP.
According to the American Heart Association, an estimated one in three U.S. adults have high blood pressure, also known as hypertension, and an alarming one-third of those don’t even know they have it. It’s no wonder this condition has long been called “the silent killer”.
Angiotensin Receptor Blockers (ARB) block the action of angiotensin II.
As of June 2005, there didn’t appear to be much global agreement among medical experts worldwide in terms of recommended first-line therapy for treating high blood pressure. A major change is that Beta-Blockers, which have been shown to be less effective in preventing strokes and more likely to cause diabetes, are no longer recommended as a routine treatment for the majority of people with high blood pressure.
A wide variety of medications are available to medical professionals for treating high blood pressure. Other classes of medications are sometimes prescribed, the most commonly prescribed can be broken down into five different classes of medications that work in different ways to lower pressure.
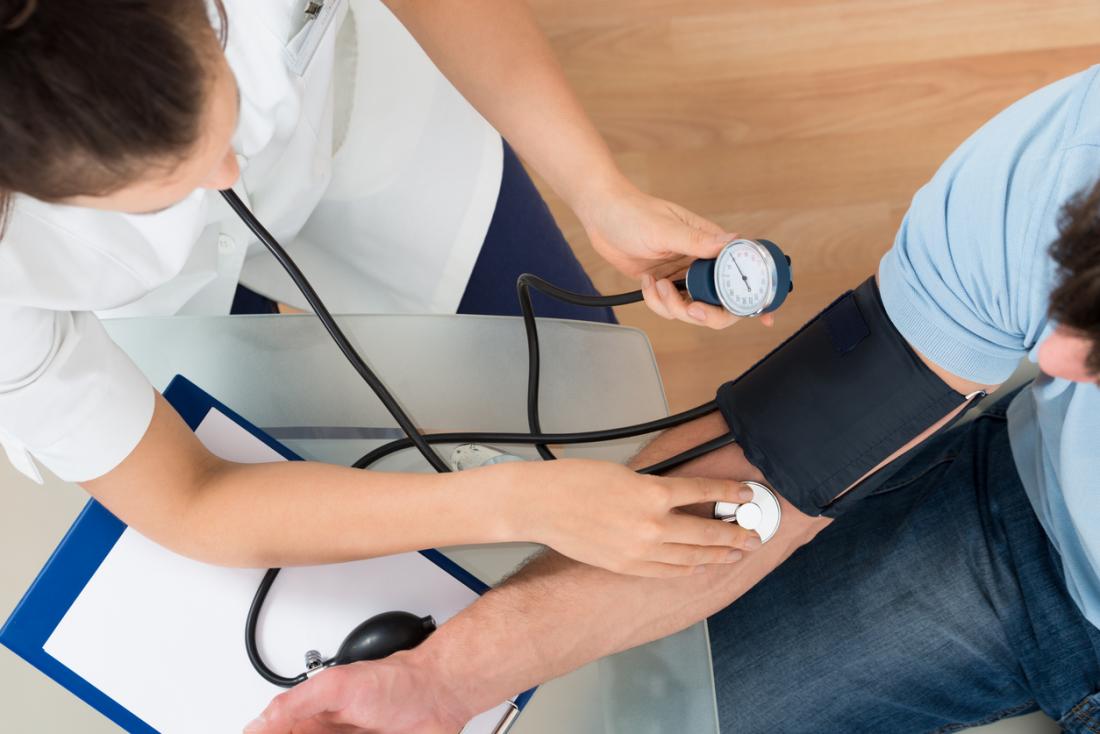
Blood pressure is the force of your blood pushing against the walls of the arteries each time your heart beats. Your blood pressure is higher each time the heart beats, pumping blood into the arteries. If your systolic pressure rises to 140 or above, or if your diastolic pressure rises to 90 or above, this is considered high blood pressure.
Beta-Blockers reduce nerve impulses to the heart and blood vessels to cause the heart to beat more slowly and with less force.
Diuretics (water pills) work in the kidney to get rid of excess water and sodium.
High blood pressure is a major risk factor for stroke, heart attack, heart failure and kidney failure. And when it exists with obesity, smoking, high blood cholesterol or diabetes, the risk of heart attack or stroke increases several times. If you don’t have high blood pressure by age 55, your chance of developing it at some point in your life is a 90 percent, according to the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute.
On January 19, 2007, Rush University Medical Center reported findings that ACE Inhibitors and ARBs prevent people from getting diabetes, and that diuretics and beta-blockers increase the chance that a person becomes diabetic. The authors pointed out that more studies are required to determine whether new-onset diabetes leads to as many heart attacks, strokes or death, as long-standing diabetes. Their data suggest that the differences between antihypertensive drugs regarding the risk for new-onset diabetes are real and are significant.
Melaleuca offers a natural high blood pressure remedy called ProStolic which interacts with a natural body enzyme much like the ACE Inhibitors and ARB medications to relax blood vessels and allow healthy blood flow. As a comparison, it might be helpful to understand how the ACE and ARB class of drugs react, as well as how the non-drug hypertension remedy ProStolic formula reacts with the body.
While most people can tolerate ACE Inhibitors, some may experience side effects such as cough, elevated blood potassium levels, low blood pressure, dizziness, headache, drowsiness, weakness, abnormal taste (salty or metallic taste), and rash.
What exactly is high blood pressure and why isn’t there a global agreement among the medical industry of for the best treatment? Learn more about the dangers of high blood pressure and commonly prescribed medications for hypertension in part 1 of our blood pressure report.
Angiotensin Converting Enzyme (ACE) Inhibitors prevent the formation of a hormone called angiotensin II, which would otherwise cause vessels to narrow.
Calcium Channel Blockers prevent calcium from entering the muscle cells of the heart and blood vessels, causing blood vessels to relax.
High blood pressure can occur in both adults and children, it is most common in those over age 35 and is most prevalent in African Americans, elderly and middle-aged people, obese people, heavy drinkers and women taking birth control pills. Many people get high blood pressure as they get older, it is not part of the aging process! Proper diet, exercise and lifestyle changes can help in prevention and lowering of blood pressure.
Commonly Prescribed Medication for High Blood Pressure
Blood pressure is the force of your blood pushing against the walls of the arteries each time your heart beats. Your blood pressure is higher each time the heart beats, pumping blood into the arteries. If your systolic pressure rises to 140 or above, or if your diastolic pressure rises to 90 or above, this is considered high blood pressure.